Table Of Contents
Tableau’s User Experience
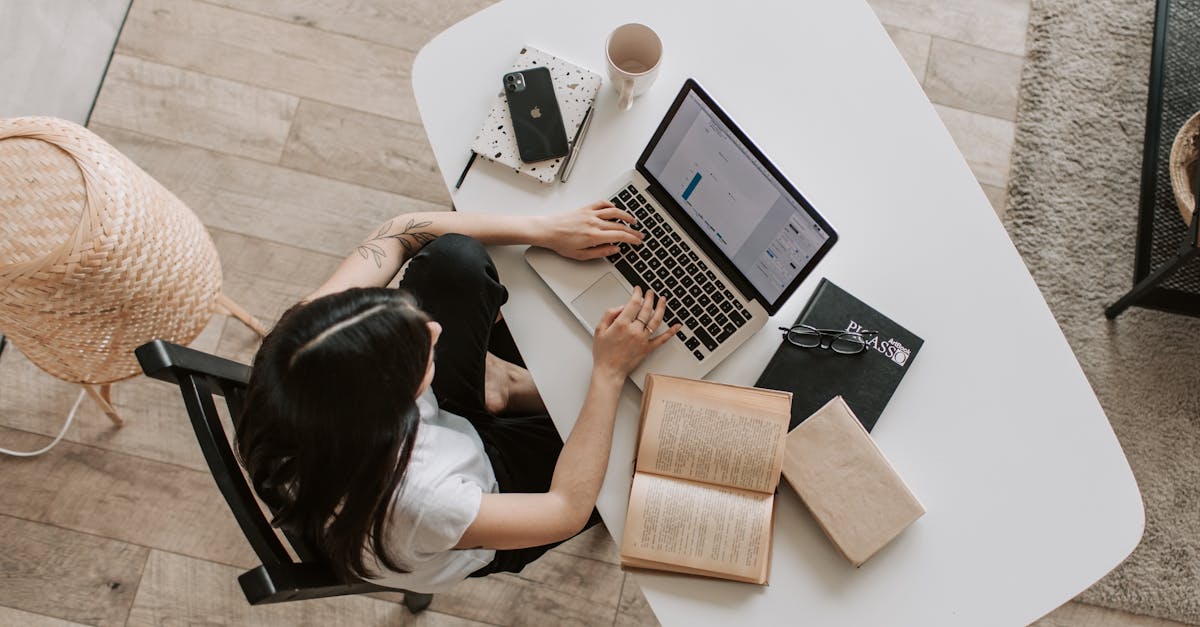
Tableau delivers a user experience that is both intuitive and visually engaging, making it accessible to individuals with varying levels of technical expertise. Users can easily navigate its interface, which allows for quick access to data manipulation tools and visualisation options. The drag-and-drop functionality facilitates the creation of custom dashboards without extensive coding knowledge. This empowers analysts to focus on deriving insights from data rather than grappling with complex software.
Incorporating Tableau into the workflow of analytics and reporting provides a seamless transition from data exploration to presentation. The platform’s emphasis on visualisation tools enhances the clarity of information, enabling users to communicate findings effectively. The integration of interactivity further enriches the experience, allowing stakeholders to explore data dynamics in real-time. This user-centric approach makes Tableau a preferred choice for businesses looking to improve their data-driven decision-making processes.
Accessibility and Ease of Use
Tableau is designed with user accessibility in mind, allowing individuals from various backgrounds to engage with data easily. Its intuitive drag-and-drop interface simplifies complex processes, making it approachable for those without extensive technical skills. Users can create interactive dashboards and visualisations with minimal training, enabling a wide range of professionals to harness the power of data. This ease of use is critical in the fields of Analytics and Reporting, where timely insights can significantly impact decision-making.
Furthermore, Tableau promotes collaborative features that enhance its accessibility within teams. Users can easily share their reports and visualisations, encouraging collective analysis and discussion. This fosters a data-driven culture across organisations, supporting the seamless integration of analytics into everyday operations. By making analytics and reporting more accessible, Tableau empowers all levels of staff to contribute to data-focused initiatives, ultimately improving overall productivity and insights.
The Importance of Data Storytelling
Data storytelling is a powerful tool that transforms raw data into compelling narratives. By combining analytics and reporting, organisations can engage their audiences more effectively. Visual elements enhance comprehension and retention, allowing stakeholders to grasp complex information at a glance. The ability to weave a story around data helps convey insights that might otherwise be overlooked in traditional reporting formats.
In today’s data-driven landscape, the significance of data storytelling cannot be understated. It goes beyond mere presentation, focusing on the context and implications of the information. By illustrating trends and patterns through visual representations, organisations can drive action and facilitate strategic decision-making. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of analytics, enabling teams to align their objectives with the broader business goals.
How Tableau Enhances Narrative Through Visuals
Tableau transforms complex data into insightful narratives through its suite of visualisation tools. The platform allows users to create interactive dashboards that highlight key metrics and trends. This visual representation aids in understanding large datasets, enabling stakeholders to grasp essential insights quickly. By presenting data in a compelling manner, Tableau encourages deeper engagement and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
With its focus on Analytics and Reporting, Tableau provides users the ability to design visualisations that support storytelling. Users can combine different data sources seamlessly, allowing for richer analysis and context. The interactivity of Tableau’s dashboards not only makes the insights accessible but also invites exploration, leading to a more dynamic understanding of the data. This approach is vital for businesses to effectively communicate their findings and strategies.
Tableau’s Application in Various Industries
Tableau finds application across numerous industries, making it a versatile tool for professionals seeking to derive insights from data. In sectors such as healthcare, financial services, and retail, organisations leverage Tableau’s robust analytics capabilities to monitor performance, identify trends, and drive decision-making processes. The ability to create interactive dashboards allows teams to engage with data meaningfully, aligning strategies with real-time insights.
In education, Tableau empowers institutions to track student performance and operational efficiency. Its user-friendly interface simplifies the process of visualising complex data sets, allowing educators to focus on learning outcomes rather than the intricacies of data manipulation. By integrating Tableau into their workflows, various industries enhance their Analytics and Reporting capabilities, fostering a culture of informed decision-making across all levels of the organisation.
Use Cases Across Different Sectors
Tableau's versatility as a data visualisation tool makes it a valuable asset across a range of industries. In the healthcare sector, professionals leverage its capabilities to monitor patient outcomes, track resource allocation, and analyse treatment effectiveness. Its intuitive dashboards simplify complex datasets, allowing healthcare providers to focus on improving patient care through data-driven decisions. In the retail industry, businesses utilise Tableau to analyse sales trends, customer behaviour, and inventory management. These insights foster a better understanding of market dynamics, enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Moreover, Tableau's role in finance cannot be understated. Financial analysts use the platform to create detailed analytics and reporting, providing stakeholders with insights into asset performance, risk management, and investment strategies. This ability to visually interpret financial data supports informed decision-making and drives strategic planning. Education and non-profit sectors also benefit from Tableau, using it to assess programme effectiveness, track fundraising efforts, and communicate outcomes to stakeholders. Each of these examples illustrates how Tableau's robust analytics and reporting tools empower organisations to turn data into actionable insights.
FAQS
Is Tableau considered a reporting software?
Yes, Tableau is considered a reporting software as it allows users to create and share interactive reports and dashboards that visualise data insights effectively.
What are the main features of Tableau that support reporting?
Tableau offers features such as drag-and-drop functionality, interactive dashboard creation, data blending, and a variety of visualisation options, all of which enhance its reporting capabilities.
Can Tableau be used for real-time reporting?
Yes, Tableau can connect to live data sources, enabling real-time reporting that helps businesses make timely decisions based on the latest data.
How does Tableau differ from traditional reporting tools?
Unlike traditional reporting tools that often provide static reports, Tableau allows for dynamic visualisations and interactive dashboards, enabling users to explore data in a more engaging way.
Is Tableau suitable for non-technical users for reporting purposes?
Absolutely! Tableau is designed with an emphasis on accessibility and ease of use, making it suitable for non-technical users to create reports without needing extensive programming skills.