Table Of Contents
Analytics Processes
Analytics processes encompass a series of steps designed to collect, analyse, and interpret data effectively. These processes often begin with data gathering, where raw information is sourced from various inputs. Following this, data cleansing and preparation ensure accuracy, helping to eliminate inconsistencies and errors. Once the data is ready, analytical techniques are applied to derive meaningful insights that aid in decision-making. This structured approach is essential for organisations that wish to leverage their data for strategic advantages.
In contrast, reporting serves as a means to communicate findings derived from analytics processes. It involves summarising key insights and presenting them in a format that is easily digestible for stakeholders. Different types of reports can cater to diverse audiences, ranging from detailed internal documents to high-level executive summaries. The synergy between analytics processes and reporting is crucial, as it transforms raw data analysis into actionable intelligence. By effectively managing both analytics and reporting, organisations can foster a data-driven culture that enhances performance and accountability.
Steps Involved in Performance Analytics
Performance analytics involves several critical steps that ensure data is effectively utilised to drive decision-making. The process typically begins with defining the objectives and goals that guide the analysis. This initial phase focuses on identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the business’s strategic aims. Once the KPIs are established, data collection follows, requiring a systematic approach to gather accurate and timely information from various sources.
After data collection, the next step involves data analysis, where trends, patterns, and anomalies are examined to derive insights. This analysis often employs statistical techniques and analytical tools, allowing organisations to interpret the data meaningfully. Visualisation plays a vital role in conveying these insights, often through dashboards or reports that facilitate understanding and support strategic decisions. Ultimately, the integration of analytics and reporting ensures that performance is monitored continuously, providing essential feedback to enhance strategies and outcomes.
Types of Reports
Reporting serves as a mechanism to communicate data in a structured format, allowing stakeholders to access essential information efficiently. Various types of reports can be generated based on the specific needs of businesses, organisations, or departments. While some reports provide a snapshot of past performance, others may focus on forecasting future trends. The distinction often lies in the intended audience and the level of detail required, with operational reports typically aimed at daily tasks and strategic reports designed for long-term decision-making.
Analytics and Reporting often complement each other to enhance decision-making processes. Descriptive reports summarise past performance using historical data, while analytical reports interpret this data to provide insights. Another type, diagnostic reports, goes a step further by exploring the reasons behind certain outcomes, thus aiding in understanding the factors influencing performance. Ultimately, selecting the appropriate report type depends on the specific objectives and questions that need to be addressed within the analytics framework.
Categories of Reporting Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques exist to facilitate effective reporting, each designed to cater to specific needs of organisations. Traditional reporting tools often include spreadsheets and presentation software, which allow for the manual compilation and visualisation of data. More advanced options encompass business intelligence platforms, which automate data collection and offer real-time insights, making it easier for businesses to derive value from their data.
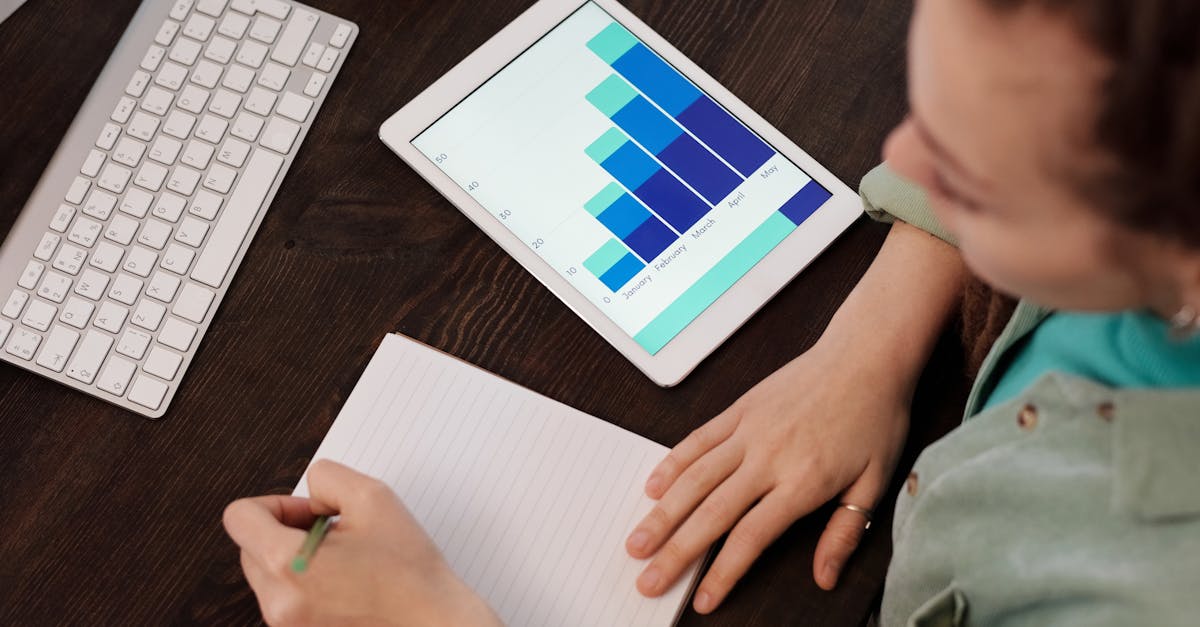
In the realm of Analytics and Reporting, dashboards have gained significant traction. These provide an at-a-glance view of key metrics, allowing stakeholders to monitor performance without delving into extensive reports. Additionally, customised reporting tools enable organisations to create specific reports tailored to their unique requirements, enhancing clarity and facilitating informed decision-making across various levels of the business.
Metrics and KPIs
Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as essential benchmarks in both analytics and reporting processes. They provide clarity on organisational performance and help quantify success in various areas. Metrics can encompass a wide range of data points, from financial figures to customer engagement levels. Conversely, KPIs are specifically chosen to reflect critical business objectives and strategic goals. They help stakeholders focus on what matters most, ensuring that the organisation remains aligned with its vision and targets.
In the context of analytics and reporting, understanding the nuances between general metrics and KPIs is vital. Analytics encompasses a broader analysis that can reveal trends and insights over time, while reporting typically presents periodic snapshots of performance. KPIs facilitate an ongoing evaluation of success in relation to strategic priorities. By regularly monitoring these indicators, businesses can adapt their strategies, ensuring they are responsive to emerging trends and challenges in the market.
Key Performance Indicators in Performance Analytics
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) play a crucial role in performance analytics, serving as measurable values that determine an organisation’s progress towards its goals. These indicators offer insight into various aspects of performance, enabling businesses to assess efficiency and effectiveness within their operations. By tracking KPIs, organisations can identify trends over time and make data-driven decisions that align with their strategic objectives. This practice fosters an environment of continuous improvement and accountability, driving teams to achieve optimal results.
In the context of analytics and reporting, KPIs are often customised to reflect the unique goals of an organisation. Common examples include revenue growth, customer satisfaction scores, and operational efficiency metrics. These specific indicators not only help in monitoring performance but also facilitate comparisons over different periods or against industry benchmarks. By employing a robust set of KPIs, businesses can ensure that their performance analytics is both comprehensive and aligned with their broader organisational strategies.
FAQS
What is the main difference between reporting and performance analytics?
Reporting primarily focuses on presenting historical data and insights in a structured format, while performance analytics goes a step further by analysing that data to evaluate performance and inform decision-making.
Why is performance analytics important for businesses?
Performance analytics is crucial for businesses as it helps identify trends, measure the effectiveness of strategies, and guide future actions by providing actionable insights derived from data analysis.
What types of reports are commonly used in business analytics?
Common types of reports include operational reports, financial reports, and compliance reports, each serving to present specific data sets and metrics relevant to different business functions.
How are metrics and KPIs related to performance analytics?
Metrics are quantifiable measurements used to track performance, while Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are specific metrics that are deemed critical for assessing the success of an organisation's objectives in performance analytics.
What tools can be used for reporting and performance analytics?
There are various tools available for reporting and performance analytics, including business intelligence software, dashboard applications, and data visualisation tools, each catering to different analytical needs and reporting formats.